Ensuring Compliance: Employer Responsibilities under the 183 Days Rule
In the realm of international employment, employers play a critical role in ensuring compliance with the 183 days rule, which determines the tax residency status of their workforce. Understanding and fulfilling their responsibilities in this regard is paramount for both the employer’s reputation and the well-being of their employees.
Educating Employees on Tax Implications
Employers have a responsibility to educate their employees about the implications of the 183 days rule and its impact on their tax residency status. Providing comprehensive guidance and resources can empower employees to make informed decisions about their international assignments and ensure adherence to global tax regulations.
Facilitating Compliance Monitoring
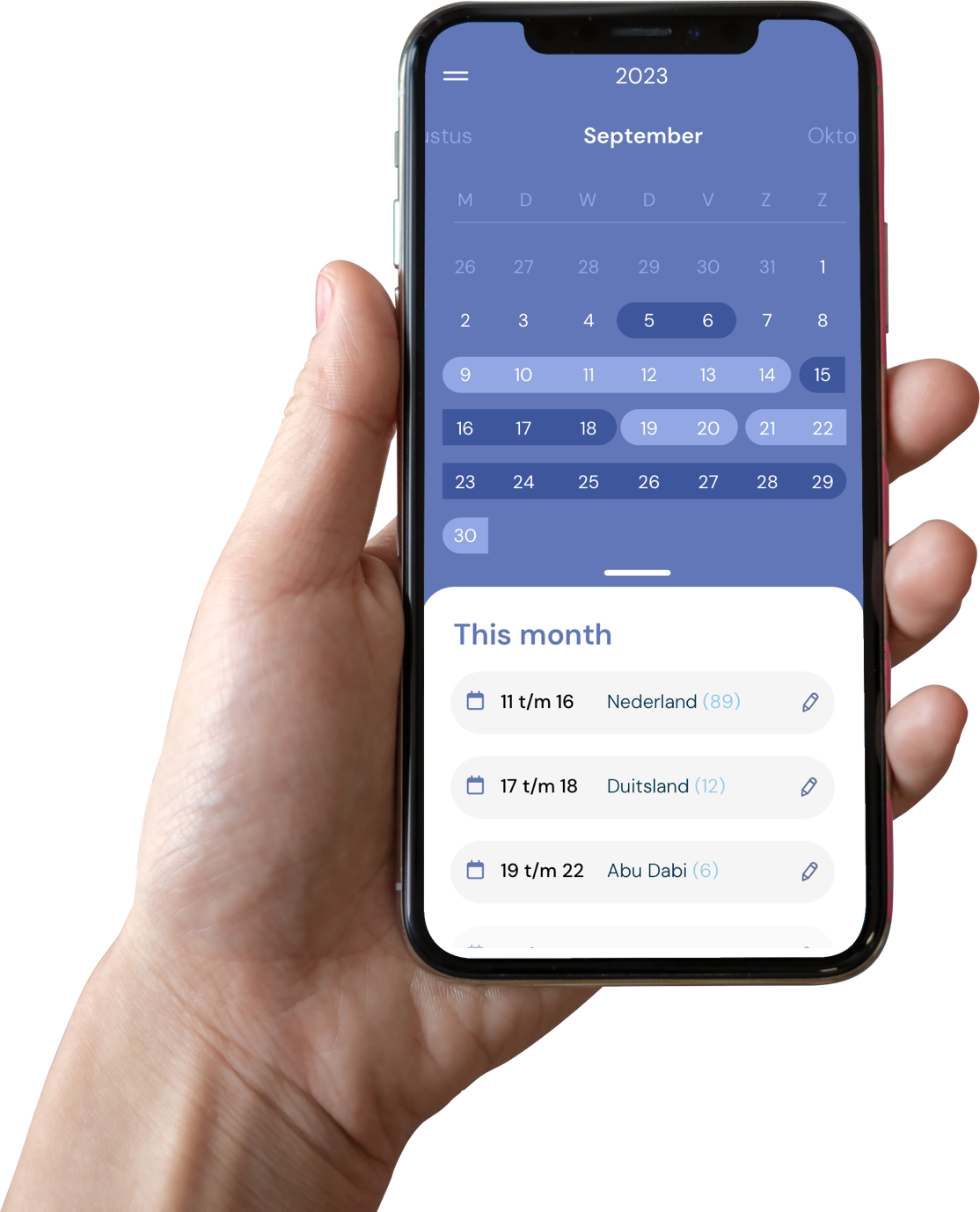
Employers should facilitate the monitoring of employee stays in different countries, especially when managing a globally distributed workforce. Implementing tracking mechanisms and streamlined reporting systems can assist employees in accurately recording their days spent in various jurisdictions, thus ensuring compliance with the 183 days rule.
Offering Tax Advisory Support
Employers bear the responsibility of providing access to professional tax advisory services for employees navigating the complexities of international taxation. Equipping employees with the necessary resources and expert guidance can help them navigate tax residency regulations effectively and prevent potential legal and financial repercussions.

Enabling Flexible Work Arrangements
In instances where employees engage in cross-border work or frequent international travel, employers should consider offering flexible work arrangements. These arrangements can help employees manage their schedules in a manner that aligns with the 183 days rule, thereby reducing the risk of unintended tax residency and facilitating a conducive work-life balance.
Compliance with International Laws and Regulations
Employers must stay abreast of evolving international tax laws and regulations to ensure seamless compliance with the 183 days rule. Maintaining a comprehensive understanding of the legal requirements and proactively adapting company policies and practices can safeguard the organization and its employees from potential legal consequences and financial liabilities.
Conclusion
Employers play a pivotal role in ensuring their employees’ compliance with the 183 days rule, necessitating proactive measures such as education, facilitation of monitoring, tax advisory support, and flexible work arrangements. By prioritizing these responsibilities, employers can foster a culture of compliance, bolster employee trust, and cultivate a conducive environment for international business operations and workforce management.